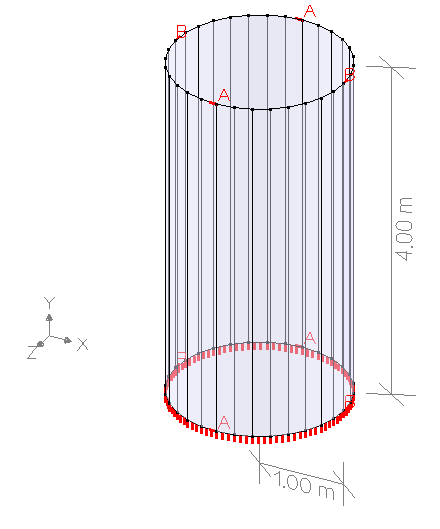
Description
| Material | Modulus of elasticity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Poisson’s ratio | |||
| Density | |||
| Geometry | Cross-section | Thickness | |
| Boundary conditions | At bottom edge | ||
| In point A | |||
| In point B | |||
| Loads | Self-weight1 | ||
| Mesh | Maximum element size | ||
| Minimum element size |
Results

Deformation ![]() in Diamonds
in Diamonds
| Point | Which result | Independent reference | Diamonds | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y=2m | stress |
0,157N/mm² | 0,157N/mm² | 0,00% |
| Y=0 | Longitudinal deformation |
0,002990mm | 0,002991mm | 0,02% |
| Y=0 | Radial deformation |
0,000449mm | 0,000442mm | -1,46% |
References
- Mécaniciens, S. F. D. (1990). Guide de validation des progiciels de calcul des structures: SSLS 09: cylindre mince sous son poids propre
- Roark, R. J., & Young, W. C. (2002). Roark’s Formulas for Stress and Strain (7th edition, Table 13.1 case 1e). McGraw-Hill Companies.
- Tested in Diamonds 2023r01.

