This article explains how to send one or nodes of a Revit to PowerConnect, using BIM Expert.
1. Preparation in Revit
The transfer is based on the analytical model. So in Revit, you need to create an analytical model first. You can use the Analytical Automation command in Revit or create the analytical elements manually. The quality and coherence (connection between elements) of the analytical model is not relevant, as PowerConnect will only take the physical model into account.
2. Send the Revit model to PowerConnect
2.1 From Revit to BIM Expert
There are 2 ways to send models from Revit to BIM Expert:- Starting in Revit: in the BIM Expert tab page, select ‘Export’.

- Starting in BIM Expert: click ‘Model > Import’ and select the Revit plugin. In case you have multiple Revit models open, BIM Expert will ask to select your model to be transferred.

2.1.1 Settings
You can have all (or a selection of) analytical elements exported. All elements is the most likely option.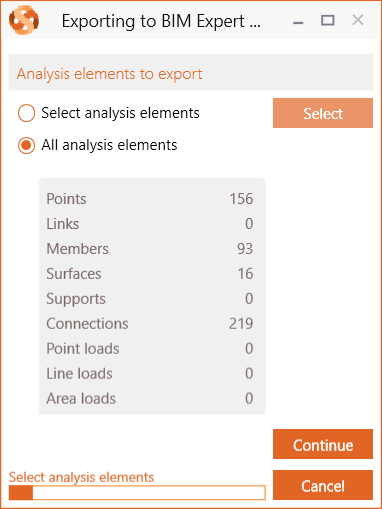 Next, the Revit sections and materials must be mapped with BIM Expert’s section and material database. BIM Expert will try to find as many automatic mapping matches as possible. In case all sections and materials find a match, you will not see any dialogs for mapping.
Next, the Revit sections and materials must be mapped with BIM Expert’s section and material database. BIM Expert will try to find as many automatic mapping matches as possible. In case all sections and materials find a match, you will not see any dialogs for mapping.
2.1.2 Material mapping
Database materials such as steel (e.g. S235, ASTM-Grades), concrete (e.g. C25/30, M50) and timber (e.g. C24, D50, GL28c) are mapped automatically. In some cases, the match is not automatically found, because the name differs (Concrete grade C25 instead of Concrete grade C25/30). In that case, you can select the correct material from the database. Tip: When searching an item in the database, type the first letters of the name to find it more quickly.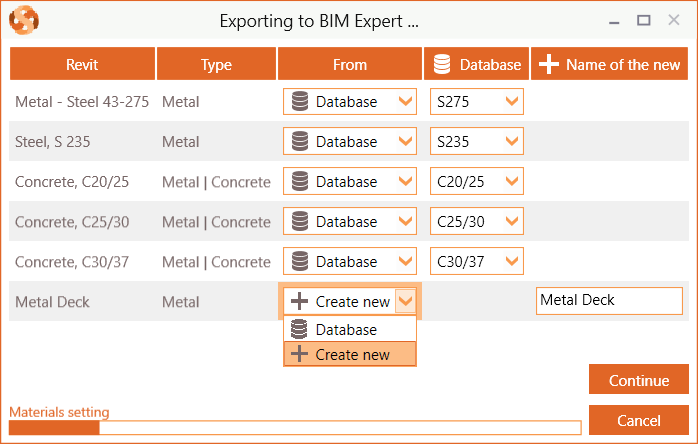 If you cannot find a suited counterpart in the BIM Expert database, the material can be added as new.
If you cannot find a suited counterpart in the BIM Expert database, the material can be added as new.
2.1.3 Section mapping
Database sections (such as I, H, UB, UC, W, C, U, O, ☐ and L sections) are mapped automatically. In some cases, the match is not automatically found, because the name differs (e.g. name is HEB300 – S235 instead of HEB300). In that case, you can select the correct cross-section from the database. Tip: When searching an item in the database, type the first letters of the name to find it more quickly. Parametric sections (e.g. rectangles, circle, trapezium, …) are not in the database. They should always be added as new.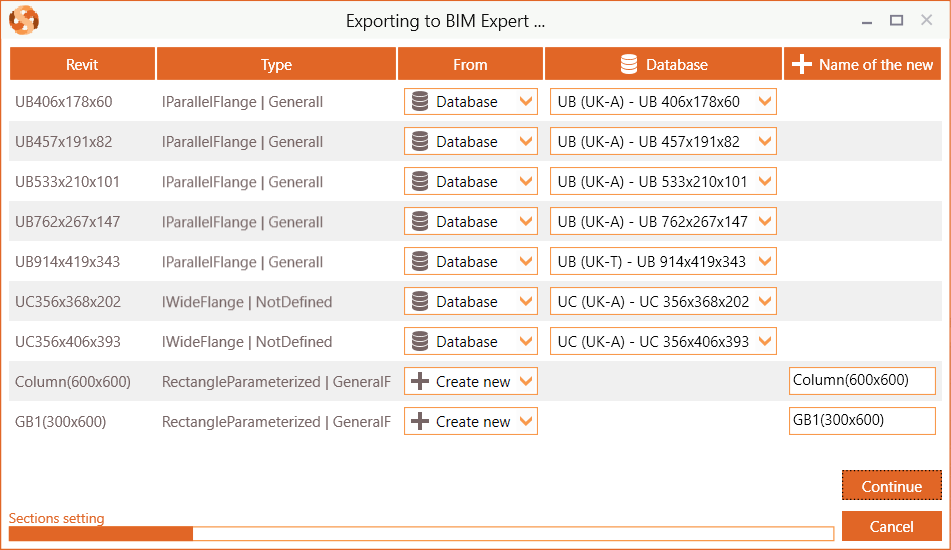 The model is now in BIM Expert.
The model is now in BIM Expert.
2.2 From BIM Expert to PowerConnect
In the Model tab, select ‘Export’. Next, choose the destination software, namely PowerConnect. Click ![]() to continue.
to continue.
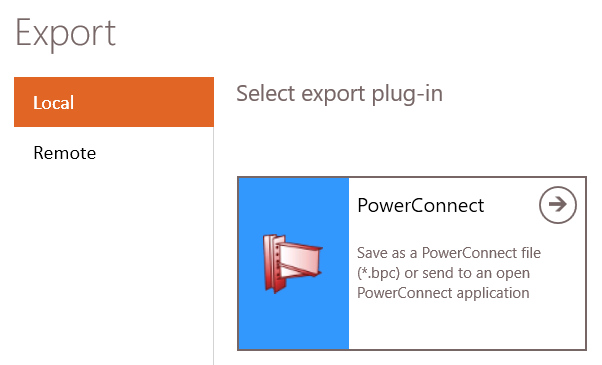
2.2.1 Settings
You can choose to either
- save the model as *.bpc-file
- send the model to the current open PowerConnect instance – you see all open instances of PowerConnect
Select your choice and click ![]() to continue.
to continue.
2.2.2 Automatic detection of connection components
BIM Expert automatically detects existing connection components in the model. You get an overview of all found connection components and whether they can be transferred to PowerConnect.
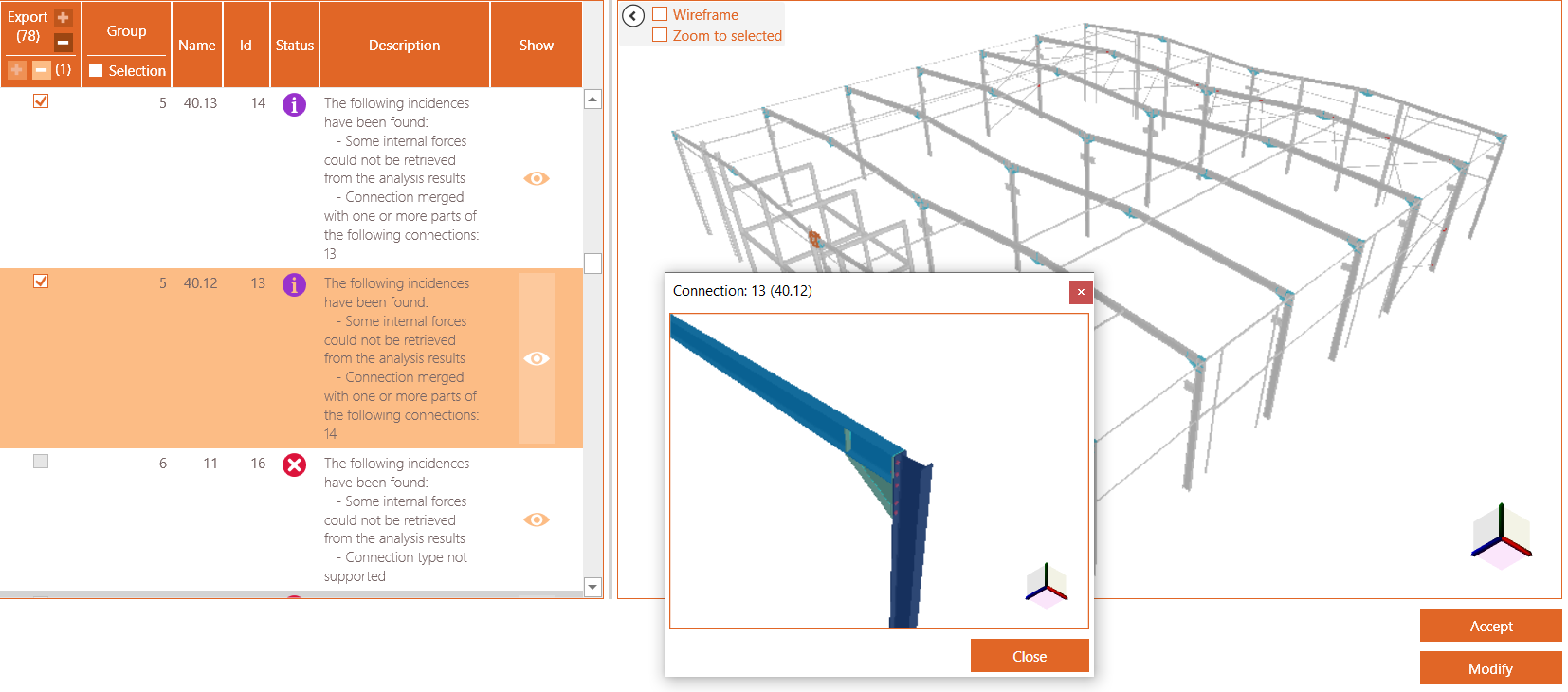
Use the eye button in the ‘Show’ column to see a detailed popup window of the connection.
Possible descriptions are
- Some internal forces could not be retrieved from the analysis results
No (or not all) internal forces are present from the source software. - The connection is identical to connection(s) {IDs} and therefore has been grouped
Identical connections will be treated as one connection. You must only calculate the connections one, with envelope forces. - Connection merged with one or more parts of the following connection: {ID}
The connection is merged with other one to create a more complex connection (e.g. two shear connections to beam-column are merged to design a double-sided shear connection) - Connection divided into <….> connections
A complex connection has been split up into smaller PowerConnect connections - The connection bars/plates with following ID’s could not be recognized: {IDs}
The connection is recognized and can be calculated with PowerConnect, execpt for these bars/plates, with given Ids - Connection type not support
This connection configuration cannot be calculated by PowerConnect, so it will not be transferred.
If no connections are found, you will see

2.2.3 Add connections manually via Connection Assembler
You can make your own connections by clicking ‘Modify’ (see image above).
In the next window, you see on the left hand side the BIM Expert model. In this window you see the regular scroll, 3D orbit and pan functions. On the right hand side, there is on top an overview of created connections and at the bottom, the ‘Create’ button to make new connections.

In the next step you choose the connection type
- Moment connections: beam-column, beam-beam, splice, beam-column-beam or CHS splice
- Shear connections: beam-column or beam-beam, beam-column-beam or beam-beam-beam
- Base plate connections
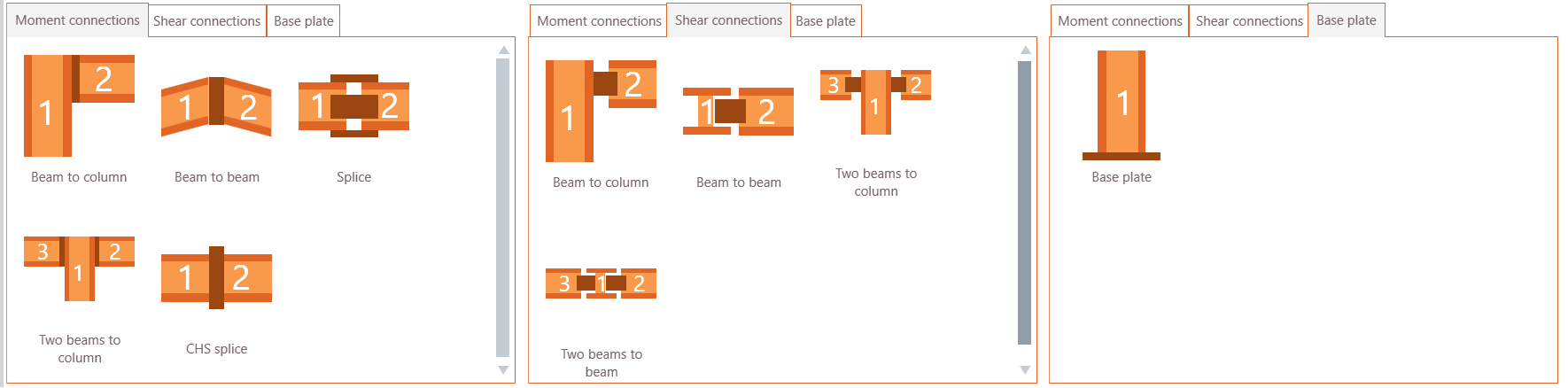
After selecting for example ‘Beam to column’ you select the column and next the beam element from the 3D image on the left hand side. Click once on the column element and next on the beam element. BIM Expert will list and indicate which connections are possible:
- Beam to column flange > possible, and marked with

- Beam to column web > not possible, and not marked – you can click the orange arrow
 at the end to fold out the details and see why this connection is not possible.
at the end to fold out the details and see why this connection is not possible.

On clicking ‘Create’, the connection is added to the list of connections on top. Having selected the beam-column type, you can now continue making this type of connections, until you click ‘Change pattern’.
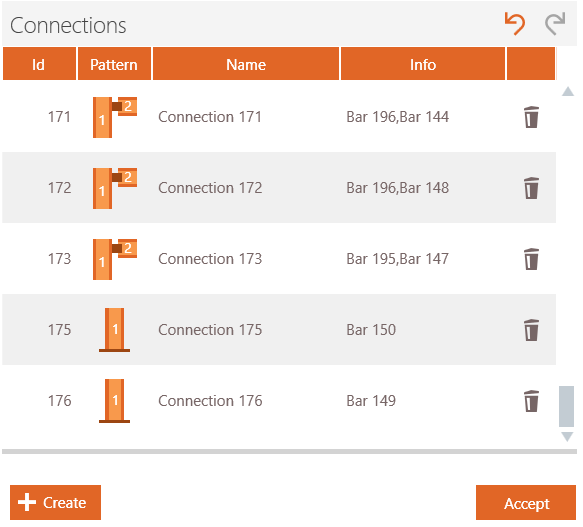
When the connection definition is finished, you click ‘Close’ and ‘Accept’ to continue to PowerConnect.
If you have chosen to open the model directly in PowerConnect, you will get a notification in PowerConnect on the right side. You can now choose to load the model or to delete it (by using the ‘x’).

3. Final steps in PowerConnect
All connections will appear in the node list on the left side (as from PowerConnect 2021). Remember that all identical connections will be grouped as 1.
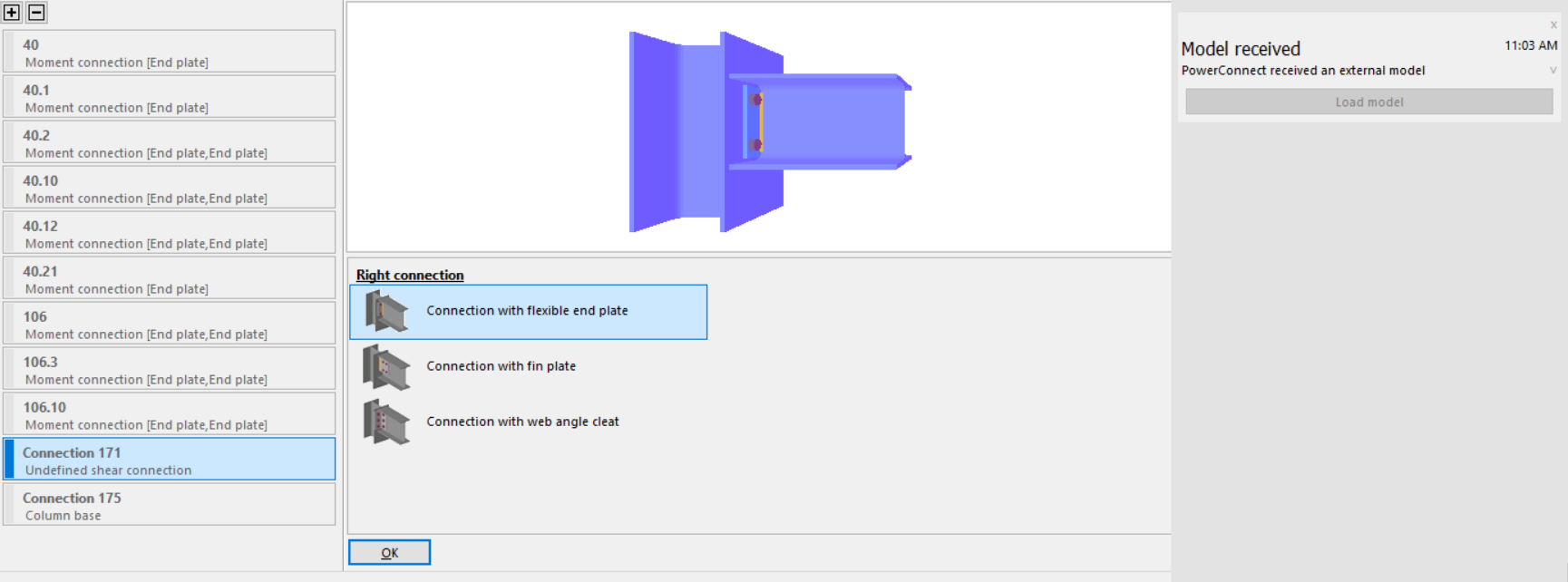
Connections made with the Connection Assembler might appear with a red bar and as ‘Undefined’. The connector type must be chosen (e.g. end plate, shear plate, welded, angles etc)
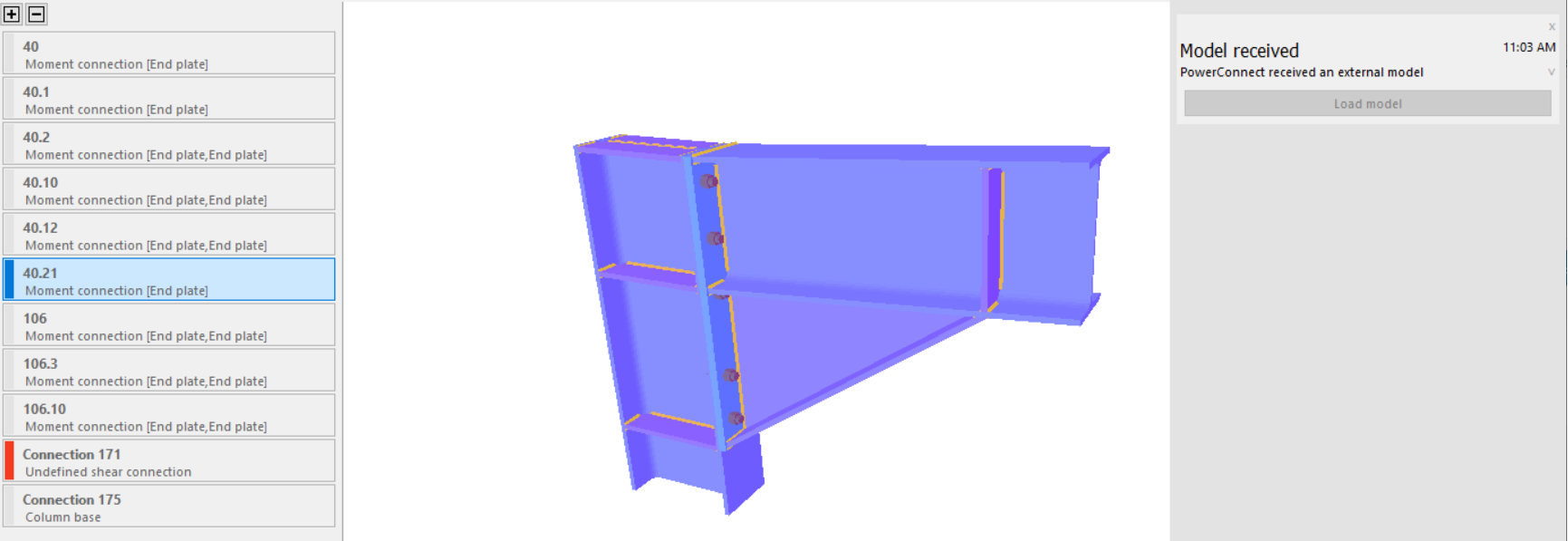
Click on this connection to set the connector.
If no loads or internal forces were transferred, you should add loads in PowerConnect, in order to have a proper design of the connections.

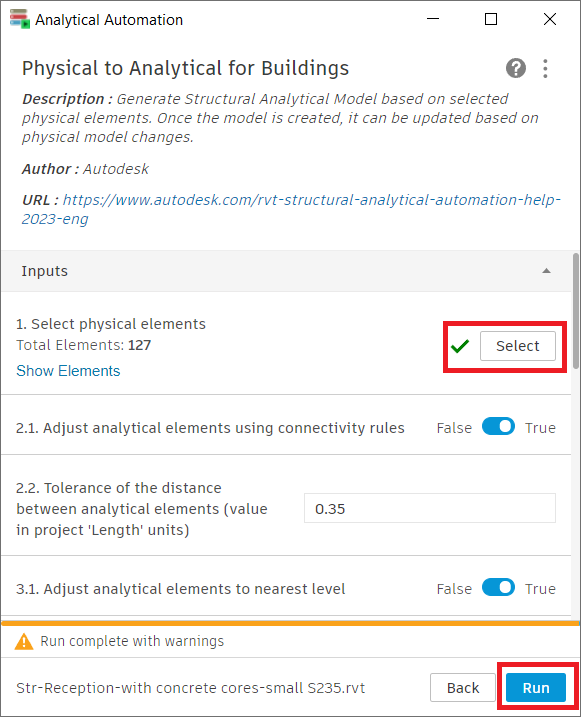
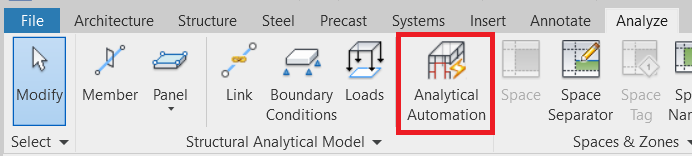 Once the Analytical Automation dialog pops up, you choose ‘Physical to Analytical’, by clicking the play button.
Once the Analytical Automation dialog pops up, you choose ‘Physical to Analytical’, by clicking the play button.